

Talk to your provider about how to take care of yourself as you recover. Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for incision care. Recovery time after surgery for a carotid body tumor is typically three to four weeks. How soon will I feel better after carotid body tumor treatment? Problems with healing at the surgical incision site.But carotid body tumor treatment can involve many blood vessels. Many people who have treatment for a carotid body tumor don’t have complications. Are there complications of carotid body tumor treatment?
#Carotid pulse Patch
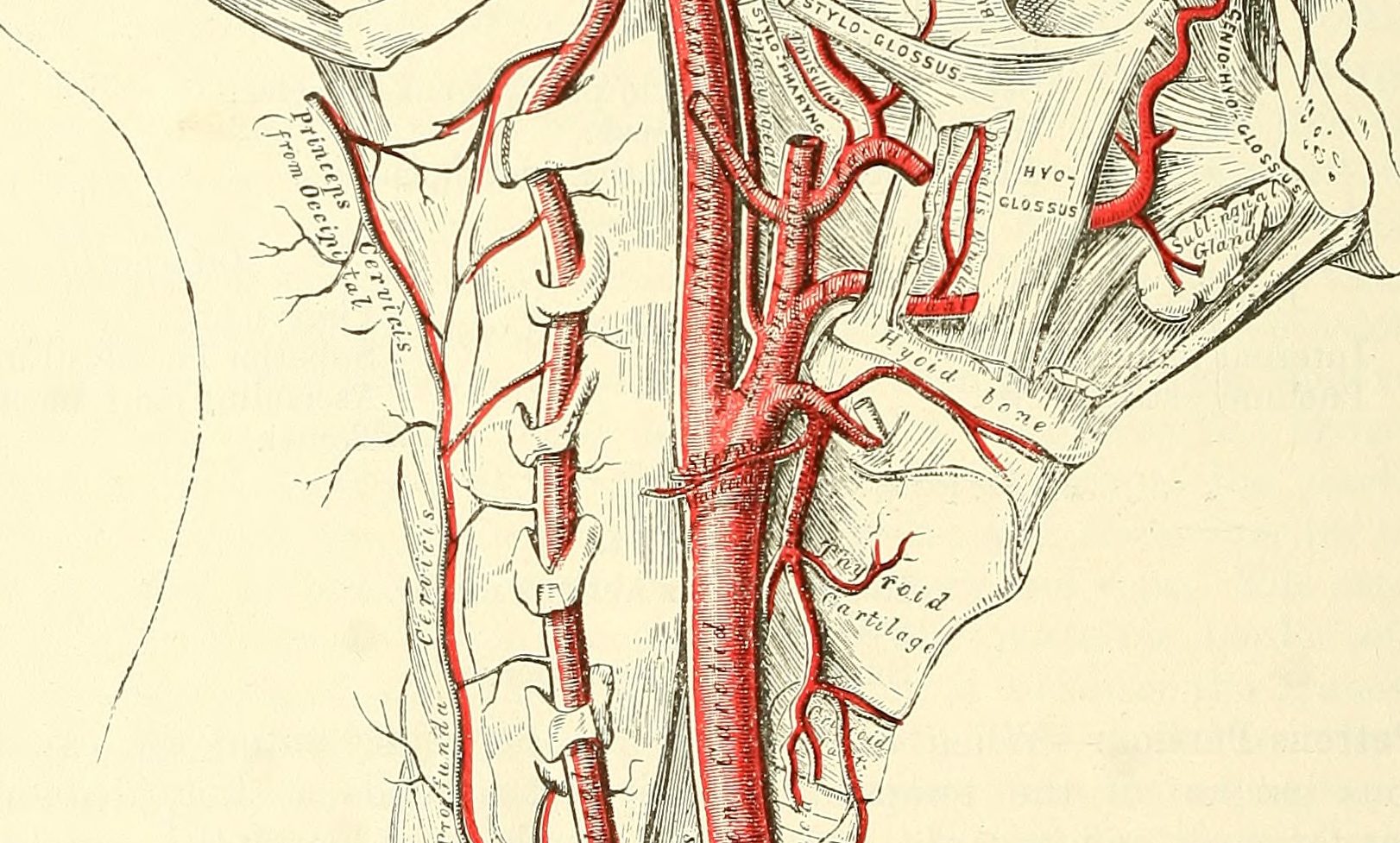
A surgeon may use a patch or graft to close the hole and restore your artery during the surgery. When providers surgically remove large carotid body tumors, a hole may remain in your carotid artery. Transcatheter embolization to stop blood flow to the tumor, which you may have before surgery to help shrink the tumor.Your healthcare provider will talk with you about your symptoms. How do healthcare providers treat carotid body tumors? To check your pulse over your carotid artery, place your index and middle fingers on your neck to the side of your windpipe. How will a carotid body tumor affect me?Ĭarotid body tumors are often painless, but your healthcare provider may want to remove the tumor because it can become large and affect the blood vessels in your neck or cause other symptoms. How rare are carotid body tumors?Ĭarotid body tumors are rare, occurring in about 1 in 30,000 people. The condition seems to be more common in women and people assigned female at birth than men and people assigned male at birth, and usually happens in people older than 20. Who can get carotid body tumors?Īnyone can get a carotid body tumor. Some studies estimate that less than 10% of carotid body tumors are malignant (cancerous). Most carotid body tumors are benign (not cancer). These arteries carry blood from your heart to your head and brain.Ī carotid body tumor is also called a carotid body paraganglioma or a carotid body chemodectoma. The results suggest that unbiased observers cannot reliably discriminate slow from "normal" velocity of rise of carotid pulse.A carotid body tumor is a mass that grows in the blood vessels near the large arteries in either side of your neck (carotid arteries).

Observer agreement was unanimous only four times and even in these instances was consistent with the recorded carotid pulse rise velocity only once. There was also no correlation of observers' ranking of rise of carotid pulse with the ranking from independent measurement of the recorded pulse rise velocity (p = 0.10 to 0.99). Now, let’s discover why the carotid artery pulses stronger on the left side. When the heart pushes oxygenated blood towards the extremities, we feel the varying volumes of blood in a rhythmic beat. Chi-square analyses yielded no significant interobserver agreements (probability 0.22 to 0.51). The work of the carotid artery pulse is to take blood that is oxygenated from the heart to the brain. The relative rate of rise of the recorded carotid pulse was represented by the angle between baseline and the initial carotid peak at a standard paper speed of 100 mm/s. To ascertain interobserver agreement (primary objective) and compare the velocity of rise of the carotid displacement (not pressure) pulse (supplementary objective), three blinded observers evaluated, ranked and palpated the velocity of rise of carotid pulse as "unremarkable," "slow" or "rapid" in 20 consecutive patients. This article reviews precordial impulses and the carotid pulse and discusses ways in which abnormal findings during the examination of these aspects of the.
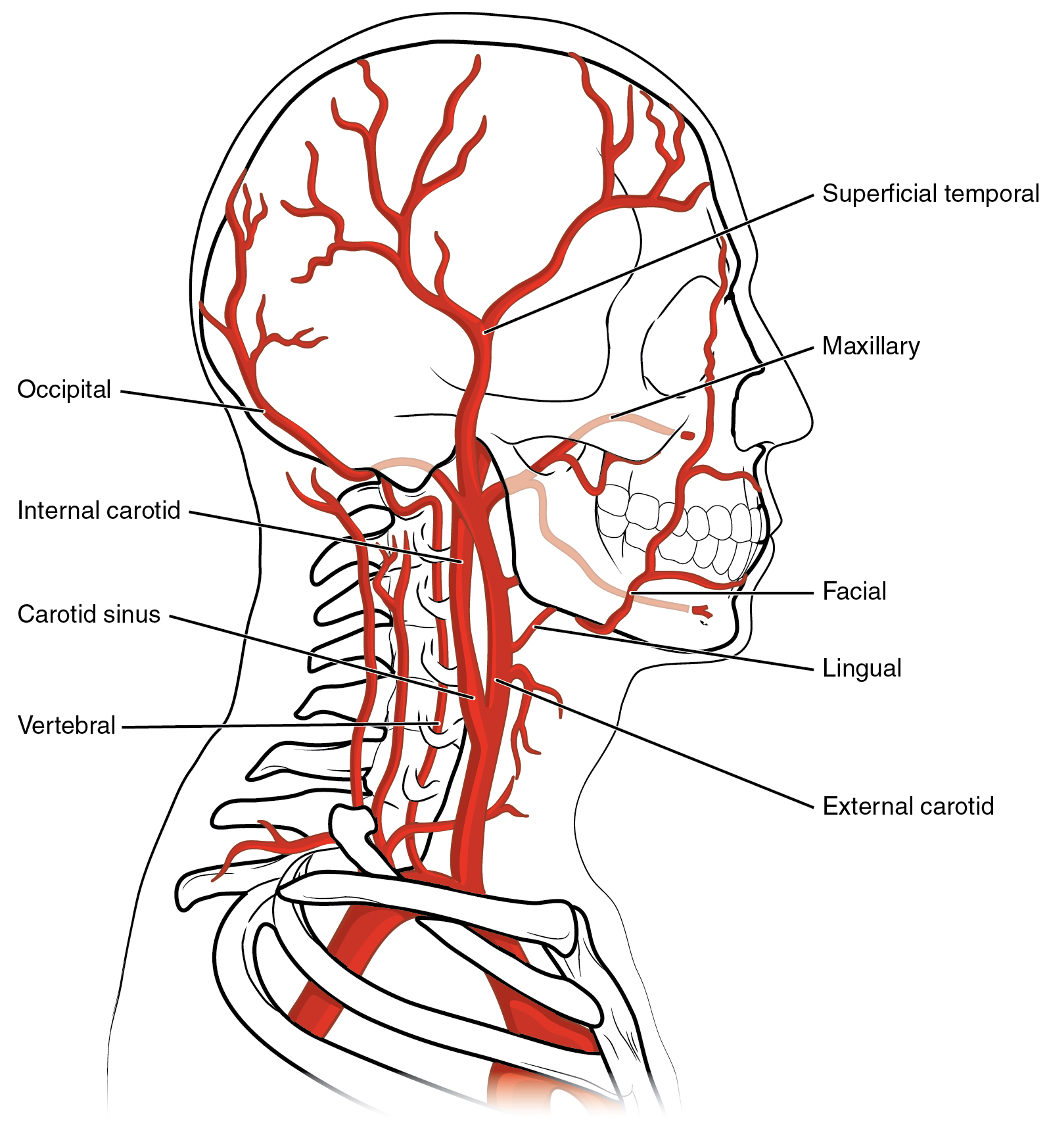
Bedside estimation of the rate of rise of the carotid pulse is a standard clinical observation whose reliability has not been determined.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
